Internet working devices
Internet working
means the high-level network that is formed by joining the several similar or
dissimilar computer networks to share some information or resources and the
word infrastructure means basic structure or features of the system.
In
terms of Information Technology, Infrastructure is the hardware used to connect
different working stations or hosts with each other.
The
hardware includes not only the computers but also all the physical devices like
telephone lines, satellites, routers, bridges, gateways, switches, hubs etc.
that help in transmission. Infrastructure also includes the software used to
send, receive data signals to/from one device to another.
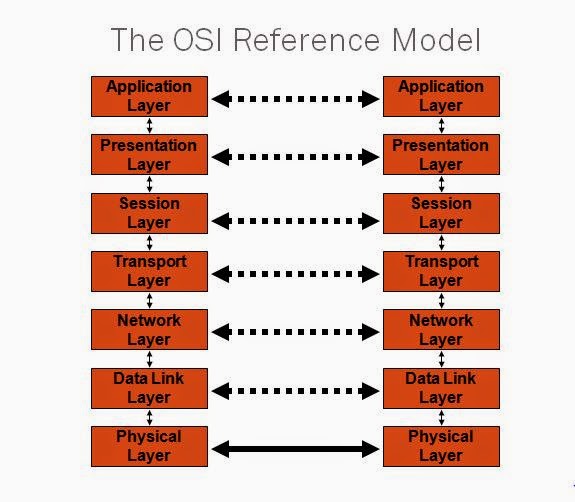
Reasons for Layering
Simplifies
the network model
Allows for
standardized interfaces to be produced by networking vendors
Increasing power and
complexity
Hubs
Bridges
Switches
Routers
Why Interconnect?
To separate / connect one corporate
division with another.
To connect two LANs with different
protocols.
To connect a LAN to the Internet.
To break a LAN into segments to relieve
traffic congestion.
To provide a security wall between two
different types of users.
To connect WLAN to LAN.
Introduction
Many times it is necessary
to connect a LAN to another LAN or to a WAN.
Computers within
a LAN are often connected using a hub.
LAN to LAN connections
are often performed with a bridge.
Segments of a LAN are
usually connected using a switch.
LAN to WAN connections
are usually performed with a router.
Hubs
A hub interconnects two or
more workstations into a local area network.
When a
workstation transmits to a hub, the hub immediately resend the data frame to all connecting links.
Hubs
expand one Ethernet connection into many. For example, a four-port hub connects
up to four machines.
Internet working
means the high-level network that is formed by joining the several similar or
dissimilar computer networks to share some information or resources and the
word infrastructure means basic structure or features of the system.
In
terms of Information Technology, Infrastructure is the hardware used to connect
different working stations or hosts with each other.
The
hardware includes not only the computers but also all the physical devices like
telephone lines, satellites, routers, bridges, gateways, switches, hubs etc.
that help in transmission. Infrastructure also includes the software used to
send, receive data signals to/from one device to another.
Reasons for Layering
Simplifies
the network model
Enables
programmers to specialize in a particular level or layer of the networking
model
Provides
design modularity
Encourages
interoperability
Allows for
standardized interfaces to be produced by networking vendors
Bridge
A bridge connects networks
and forwards frames from one network to another.
Switches
A switch is a combination
of a hub and a bridge.
It can interconnect two or
more workstations, but like a bridge, it observes
traffic flow and learns.
When a frame arrives at a
switch, the switch examines the destination
address and forwards the frame out
the one necessary connection.
Major role: isolating
traffic patterns and providing multiple access. This
design is usually done by the network
manager.
Switches are easy to
install and have components that are hot-swappable.
The backplane of a switch
is fast enough to support multiple data
transfersat one time.
Multiple workstations
connected to a switch use dedicated segments.This is
a very efficient way to
isolate heavy users from the network.
Routers (really
specialized computers)
The device that connects a
LAN to a WAN or a WAN to a WAN (the INTERNET!
– uses IP
addresses).
A router accepts an
outgoing packet, removes any LAN headers and trailers,
and encapsulates the necessary
WAN headers and trailers.
Because a router has to
make wide area network routing decisions, the router
has to dig down into the
network layer of the packet to retrieve the network
destination address.
Connections (in general)
Bridges for LANs and hubs.
Switches for LANs and workstations.
Routers for LANs and WANs (the Internet).



EmoticonEmoticon